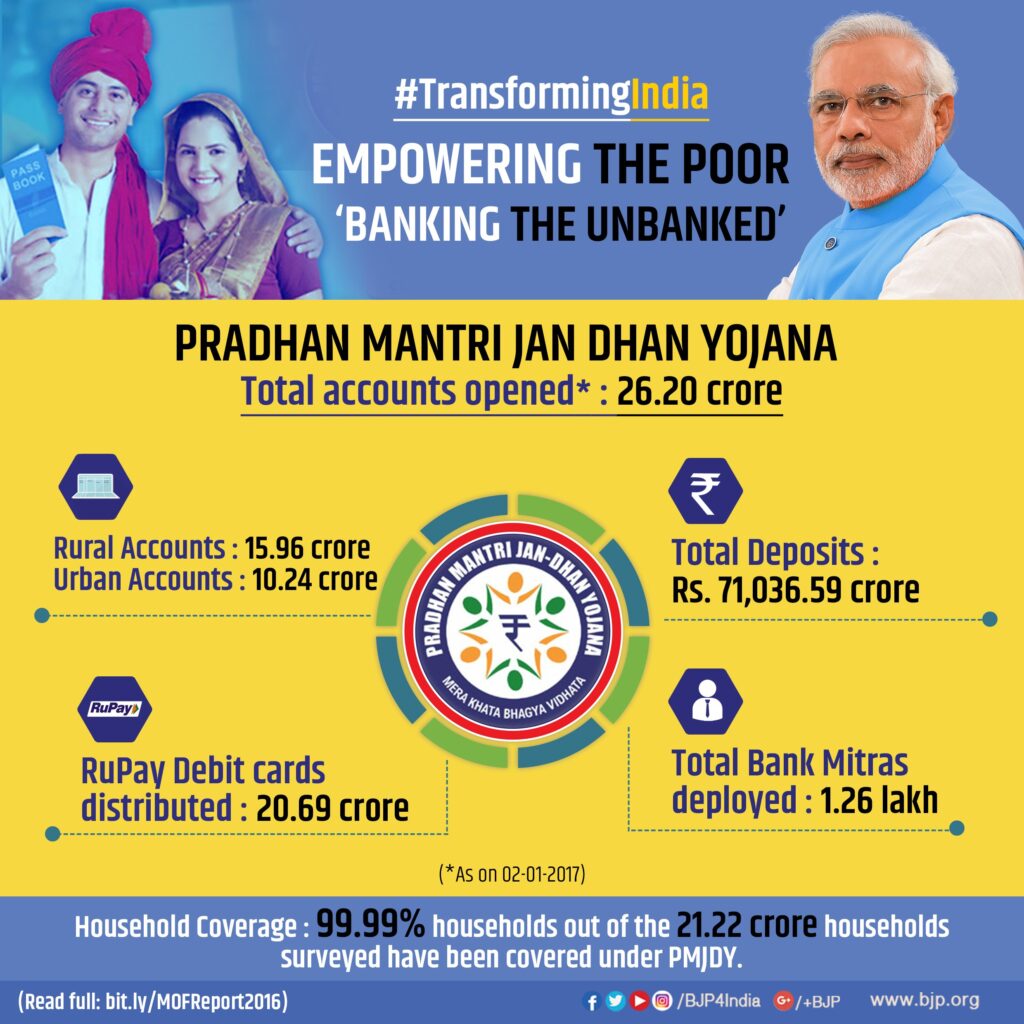
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is an apex financial inclusion initiative launched by the Government of India on 28 August 2014. The programme, is headed by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, targets the inclusion of all Indian households, mainly the poor and non-banked people from rural India, into the usage of banking facilities and financial services. PMJDY is one of the largest financial inclusion programs globally, with a design that dovetails the benefits of economic growth into the lowest strata of society.
What is Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana?
PMJDY aims to bring the entire Indian population within the formal financial system so as to include every citizen irrespective of their socio-economic status. The scheme aims to open basic savings bank accounts for every unbanked citizen, so that they have easy access to these services, such as saving, credit, insurance, and pension. Reducing reliance on informal moneylenders and other unregulated financial actors for accessing the basic financial services will benefit millions of Indians whose economic security will be improved.
The PMJDY aims to cover the entire population with at least one bank account; therefore, each household must have access to at least one bank account, thus granting broader financial literacy, security, and economic empowerment.
ALSO READ:
https://samacharpatrika24.com/viksit-bharat-by-2047/
Major Goals of PMJDY
The major goals of PMJDY are:
- This aims at making basic banking services and savings, credit, remittances, and insurance available to every household. The PMJDY seeks to bring the unorganized population into the formal fold of the economy by bringing them under formal financial services.
- Financial Literacy and Empowerment: One of the main focus areas of the scheme is financial literacy/empowerment, showcasing how people can handle their finances, save money, and use banking services. The scheme puts greater emphasis on developing financial skills among the underprivileged and economically weaker sections of society.
- Low Cost Banking: PMJDY makes opening a bank account free of charge and therefore affordable to even the most ill-willed citizen among them. In addition to this, the accounts offer zero minimum balance requirements, debit cards, and overdraft facilities.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): PMJDY provides an avenue for the Government to directly transfer subsidy and welfare schemes into the bank account of the beneficiary, eliminating the middleman and leakage in the system. It ensures timely, transparent, social welfare schemes of pensions, scholarships, and subsidies, among others.
Key Features of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
The extent and the reach of PMJDY are unmatched, and the advantage provided to account holders is too great an array of benefits:
- Zero Balance Accounts: One of the most attractive features of PMJDY accounts is that they can be opened without any requirement of maintaining a minimum balance. This removes one of the major deterrents that disqualifies the financially less privileged from using formal banking systems.
- RuPay Debit Card: Each account holder shall be issued a RuPay debit card in order to enable him to withdraw cash, make payments, etc. RuPay is India’s domestic card scheme for the promotion of cashless transactions.
- Accidental Insurance Cover: PMJDY account holders obtain accidental insurance cover of Rs. 2 lakh linked to RuPay debit card, so that economic vulnerability in case of death or injury by accidents is financially protected.
- Overdraft Facility: The eligible account holders under the scheme will be provided an overdraft facility of up to Rs. 10,000 per account. An overdraft facility is a micro-credit facility that helps account holders meet their expenses due to emergency requirements or short-term credit needs.
- Life Cover on Opening New Accounts of PMJDY: New accounts open under PMJDY will also receive a life cover of Rs. 30,000. With this, while opening new accounts under PMJDY, they along with their families will have additional financial security.
- Pension and Insurance Schemes: PMJDY is aligned with other government initiatives, including the Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) and the Atal Pension Yojana (APY), which enables account holders to receive low-cost life insurance and pension products.
Success Stories of Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
Since its launch in 2014, PMJDY has become a roaring success story, bringing millions of previously uninsured Indians into the banked sector. Some of the key success stories include:
- Huge Account Openings: So far, the number of Jan Dhan accounts opened till date has exceeded 500 million, covering the maximum part of rural and urban poor population groups. In fact, 55% of all accounts are of women holding accounts, thus encouraging women financially.
- Financial Inclusion Increased: The impetus initiated by PMJDY has not only enhanced financial inclusion in the entire Indian map but particularly in rural India. From a few thousands, the numbers of households having access to formal banking have swollen multifold, saved money, got access to credit, and so on, participating in the economy.
- Direct Benefit Transfers: The most relevant ways in which PMJDY has streamlined government welfare schemes is by allowing direct subsidies and direct benefit transfers to the accounts of the beneficiaries, thereby reducing leakages and corruption. Millions of account holders under the Jan Dhan scheme received emergency financial assistance from the government during the pandemic year, thus making it one of the most important schemes to be used at distressed times.
- Digital and Cashless Economy: PMJDY has enabled debit cards and cashless transactions, in turn facilitating the country’s march toward a Digital India. Millions of customers of Jan Dhan are online today making payments and transfers on their debit cards.
- Empowerment of Marginalized Groups: The PMJDY has empowered millions of the marginalized and economically weaker sections of society by providing them banking services that were untouchable till date. It has enabled millions of Indians to become financially self-sufficient through financial education.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite its success, the PMJDY scheme is facing some challenges:
- Dormant Accounts: Many Jan Dhan accounts are dormant accounts, having little or no activity. It may be because account holders, in general, lack awareness or have low-income levels that may restrict them from regularly using their accounts.
- Financial Literacy Low: Despite the fact that PMJDY has successfully increased the financial literacy of people, particularly in rural areas, more initiatives have to be undertaken to make people fully aware of available financial products and services.
- Enhancing Credit Flows: Although the programme has basic banking facilities, most account-holders do not enjoy credit access at low rates. Micro-credit and other credit delivery mechanisms to the poor would also be very important for their efficient empowerment.
- Infrastructure Shortages: The unavailability of adequate banking infrastructure, meagre facilities for ATMs, and internet connectivity in rural India constitute a problem for the full-possible functioning of the PMJDY.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has been a game changer in India’s journey towards financial inclusion. Bringing millions of citizens who were unbanked under the formal financial system, this scheme in this respect has played an important role in promoting economic empowerment and poverty eradication. Here, improvement access to banking services, encouragement to save, and improvement in financial literacy cannot be forgotten in determining its impact.
As the economy continues to grow in India, PMJDY would then become a very important linchpin for the country’s vision of inclusive growth and prosperity. Continued efforts in financial inclusion through increased access to credit along with the upgrading of digital banking infrastructure would make millions of Indians empowered for a much more secure financial future.

